

Disclosure: Some of the links in this article are affiliate links, which means that if you purchase through those links I will receive a small commission. For example, as Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If you decide to use these links, thank you!
Gluten-free may sound like a fad diet. However, the truth is that many people would benefit from removing gluten from their diets.
According to the New England Journal of Medicine, more than 55 diseases have been linked to gluten. A few of these diseases include irritable bowel disease,
The most
In addition, those with gluten intolerance or sensitivity, a condition that affects 6 percent of the population (18 million individuals), would also benefit from avoiding gluten.
It’s estimated that 99% of people who have either gluten intolerance or celiac disease are never diagnosed.
Gluten is a general name for the proteins found in wheat, rye, barley and triticale (a cross between wheat and rye). It helps foods maintain their shape, acting as a glue that holds food together. Gluten can be found in many types of foods, such as pasta, bread, beer, sauces, granola bars, etc.
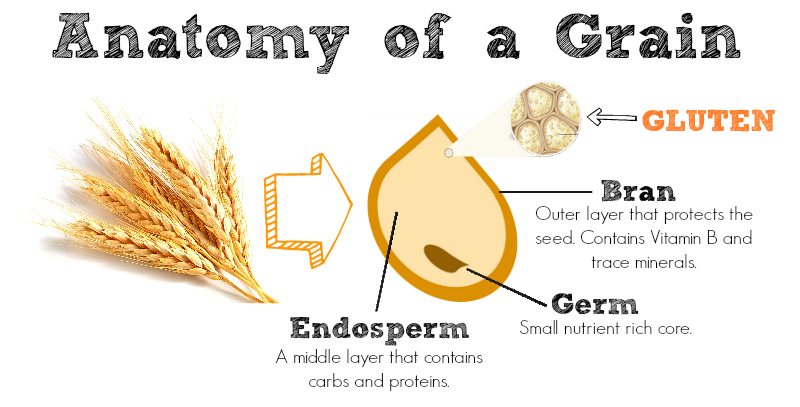
Gluten is now used to help make many highly processed chemical additives that are found in packaged foods, which can sometimes make it a challenge to follow a gluten-free diet.
Fortunately, not all grains contain gluten, so you can still enjoy many types of grains while following a gluten-free diet. Some examples of gluten-free grains are sorghum, millet, brown rice, oats, buckwheat, wild rice, amaranth, quinoa, corn (polenta) and teff.
It’s important to note that most commercial grains are processed in facilities that also process wheat, barley, and rye. The gluten in these ingredients can contaminate grains that are naturally gluten-free.

Contamination can also happen in the field when they are grown next to fields of wheat. So, it’s best to completely avoid conventionally grown and processed gluten-free grains, such as oats. When purchasing grains make sure that the bag or box states that they are certified gluten-free.
Celiac disease is a chronic digestive disorder resulting from an immune reaction to gliadin, a gluten protein. Unlike celiac disease, both gluten sensitivity and gluten intolerance do not cause damage to the lining of the small intestine. However, the body does identify gluten as a foreign invader which triggers the launch of an immune response.
Inflammation is part of that response and can contribute to digestive symptoms, such as bloating and abdominal discomfort. Frequent gluten consumption paired with gluten sensitivity or intolerance may contribute to other little-known gluten intolerance symptoms that I will explain in this post.
These symptoms should not be ignored due to the impact they may have on your quality of life and health. Knowing the symptoms and recognizing if you have them is the first step to begin feeling better.

If you have one or more of the following symptoms it could be a sign that you have a gluten intolerance.
Gluten intolerance can cause you to experience brain fog or feeling like you can’t think clearly. People who experience brain fog may have difficulty remembering things or focusing.
Research suggests that up to 75 percent of those with an anemia diagnosis may be gluten intolerant. Gluten intolerance can interfere with the uptake of iron from food, causing malabsorption of this important nutrient.
Many gluten-intolerant individuals report feeling tired and fatigued, especially right after eating gluten. A symptom of gluten intolerance can also include muscle fatigue.
Studies have shown that gluten-intolerant individuals may be more prone to migraines than others. If you have regular headaches or migraines without any apparent cause, you could be sensitive to gluten.
If you have gluten intolerance you may experience a problem with skin conditions, such as extra dry skin, rashes, acne, and patches of eczema.
Gluten negatively influences your gut microbiome and may directly influence the development and progression of autoimmune disease.
Gluten is structurally similar to a number of your body’s tissues, particularly your thyroid. If you have
Digestive issues such as gas, bloating, diarrhea and even constipation can be a sign of gluten intolerance. Stomach pain, such as nausea and abdominal cramps, after eating something containing gluten is the most common symptom of gluten intolerance.
Mood changes, or feeling an increase in depression and/or anxiety after eating gluten-containing foods is a symptom of gluten
Gluten exposure may cause inflammation, which can results in swelling or pain in your joints such as fingers, knees or hips.
Another little known symptom of gluten intolerance is neuropathy, which involves numbness or tingling in the arms and legs. Individuals with celiac disease and gluten sensitivity seem to be at a higher risk of experiencing arm and leg numbness.
If you experience any of these symptoms after eating foods that contain gluten, it is very likely that you are gluten intolerant. It is important to note that some people have an immediate reaction to gluten. However, if a person’s small intestines are capable of
The single best way to determine if you have an issue with gluten is to eliminate gluten from your diet. The general recommendation with any suspected food sensitivity is to eliminate it from your diet for at least 2 to 3 weeks and then reintroduce it. However, gluten is a very large protein and it can take months and even years to clear from your system so the longer you can eliminate it from your diet before reintroducing it, the better. I would recommend eliminating gluten for at least 4 to 6 weeks while tracking your symptoms.
The good news is that the symptoms of gluten intolerance can improve or be completely eliminated if you stick to a gluten-free diet.
If you know a friend or family member that would benefit from this information please share this with them. Also, to spread
*Please note that the information in this blog post should not be used to diagnose, treat, prevent or cure any disease or condition. This information is not a substitute for medical advice from your health care professional. For more details see my medical disclaimer here.